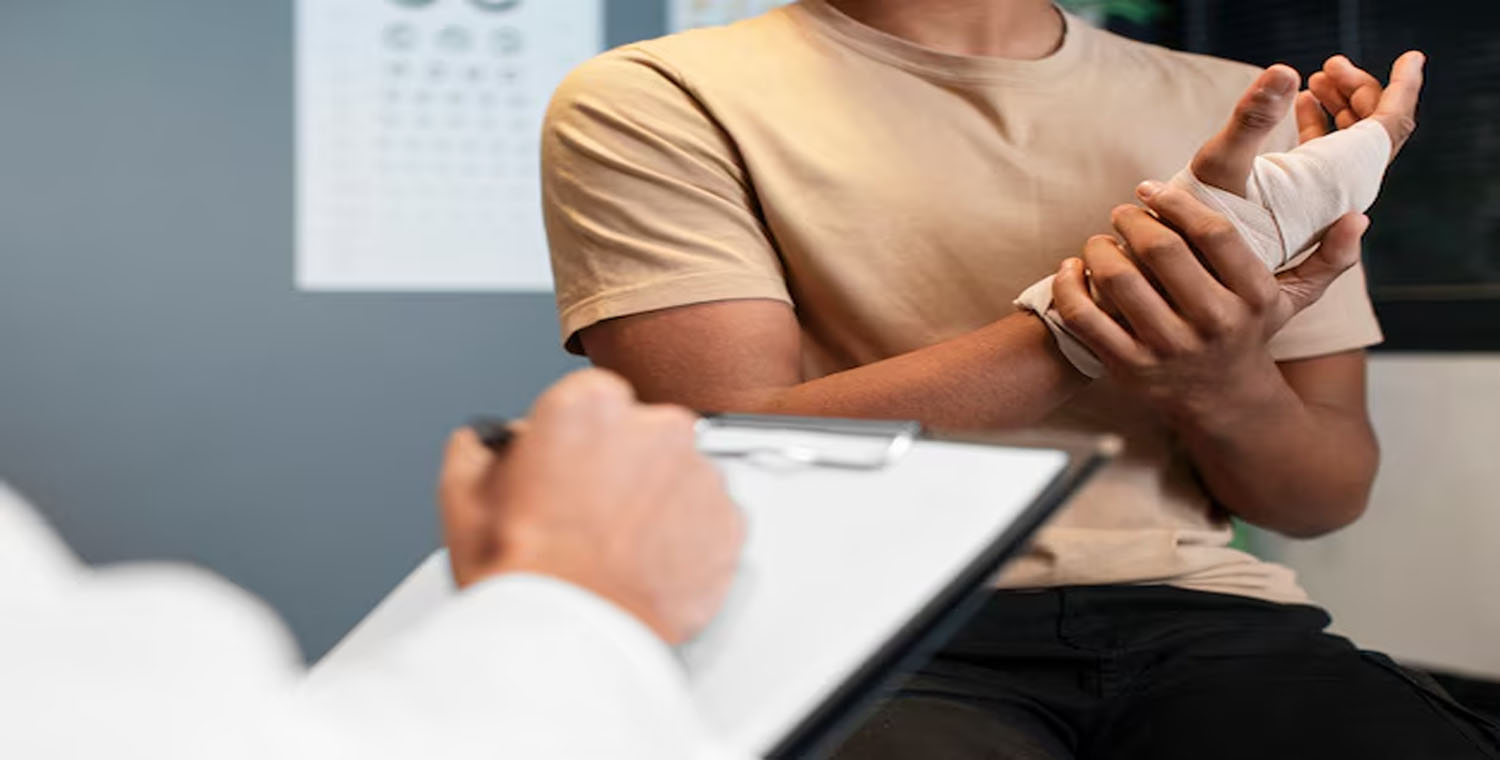
A “pouce fracturé“, or a fractured thumb, is one of the more common hand injuries that can occur due to a variety of causes. Whether it’s the result of an accident, sports injury, or a fall, a broken thumb can be both painful and debilitating. The thumb plays a crucial role in hand function, as it is essential for gripping, holding, and performing numerous everyday tasks. Therefore, any injury to this important digit can impact one’s quality of life.
In this article, we will take an in-depth look at what a pouce fracturé is, its causes, the symptoms to look out for, treatment options, and the recovery process. Whether you are dealing with a thumb fracture or simply want to learn more about this type of injury, this guide will provide you with essential knowledge to understand and address a pouce fracturé.
What is a Pouce Fracturé?
A pouce fracturé is simply the French term for a broken or fractured thumb. The thumb is made up of two bones in the palm (the proximal phalanx and the distal phalanx) and one bone in the wrist (the first metacarpal). A fracture can occur in any of these bones, but most thumb fractures affect the first metacarpal bone. The thumb also has ligaments and tendons that provide stability and mobility, and a fracture can involve these as well.
The thumb is essential for gripping, pinching, and performing other hand functions, so when it is broken, it can lead to difficulty performing everyday tasks such as holding a glass, typing, or even dressing. A pouce fracturé may occur in varying degrees of severity, from a hairline crack to a complete break, and treatment will depend on the type and location of the fracture.
Causes of Pouce Fracturé
A pouce fracturé can occur in many different ways. Some of the most common causes include:
1. Trauma or Impact
A sudden force or trauma is the leading cause of a thumb fracture. This can happen from:
- Falling onto an outstretched hand: One of the most common ways to break a thumb is by falling and landing on an outstretched hand. The force of the fall may cause the thumb to bend awkwardly, leading to a fracture.
- Sports injuries: High-contact sports like football, basketball, or hockey can lead to thumb fractures, especially if a player’s hand is hit with a ball or during a tackle. A thumb injury is common in sports that involve throwing or catching balls, like in volleyball or handball.
- Accidents: Everyday accidents, such as slamming a door or having a heavy object fall on your hand, can also cause a pouce fracturé.
2. Repetitive Stress
While less common than trauma, repetitive stress injuries can sometimes lead to a stress fracture in the thumb. This type of fracture often occurs due to prolonged overuse of the thumb joint or tendons, typically seen in activities like rock climbing, heavy lifting, or certain manual labor tasks.
3. Osteoporosis or Weakening of the Bones
People with weakened bones, such as those with osteoporosis, are at a higher risk of fractures. Even a mild injury can cause a bone to break if it is already brittle. In such cases, an older person might break their thumb with less force than would be required in a younger, healthier individual.
Symptoms of Pouce Fracturé
When dealing with a pouce fracturé, recognizing the symptoms early is important for getting the right treatment and care. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: The first and most noticeable symptom is pain, particularly when trying to move the thumb or apply pressure to it. The pain may be sharp and intense immediately after the injury or may worsen over time.
- Swelling: Swelling around the thumb or hand is typical of a fracture. This occurs as a result of inflammation in response to the injury. Swelling can make it difficult to move the thumb and may be accompanied by bruising.
- Deformity or Abnormal Positioning: In severe cases, the thumb may appear misshapen or out of alignment. The bones in the thumb might be displaced, or the thumb may appear bent or crooked.
- Difficulty Moving the Thumb: If you have a pouce fracturé, you may experience difficulty moving your thumb or fingers. Any movement may be painful, and in some cases, it may be impossible to perform basic tasks such as gripping or holding objects.
- Numbness or Tingling: If nerves in the hand are affected, you may experience numbness or a tingling sensation in the thumb or fingers.
If you suspect you have a pouce fracturé, it’s essential to see a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment.
Diagnosis of Pouce Fracturé
To diagnose a pouce fracturé, your doctor will typically perform a physical examination and may order imaging tests to confirm the presence and severity of the fracture. Diagnostic steps include:
- Physical Examination: The doctor will assess the injury, checking for deformity, tenderness, and range of motion. They may also gently manipulate the thumb to understand the extent of the injury.
- X-rays: An X-ray is typically required to determine the exact location and type of fracture. This will help the doctor assess whether the bones are aligned or displaced and whether surgery is necessary.
- CT Scan or MRI: In rare cases where the injury is more complex, a CT scan or MRI may be performed to obtain more detailed images of the bones, tendons, and ligaments around the thumb.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor will recommend an appropriate treatment plan based on the severity of the fracture.
Treatment of Pouce Fracturé
Treatment for a pouce fracturé depends on the type and severity of the fracture. The goals of treatment are to reduce pain, promote healing, and restore thumb function. Common treatment options include:
1. Non-Surgical Treatment (Conservative Management)
In many cases, a pouce fracturé can be treated without surgery. Non-surgical treatments include:
- Immobilization: A thumb fracture can often be treated with a splint or cast to immobilize the thumb and allow the bones to heal. The cast may cover the thumb, wrist, and sometimes the forearm, depending on the fracture’s location.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may be recommended to manage pain and inflammation. A doctor may also prescribe stronger medications if necessary.
- Cold Compresses: Applying ice packs or cold compresses to the injured thumb can help reduce swelling and manage pain. This should be done in intervals of 20 minutes at a time, several times a day, for the first few days after the injury.
- Rest and Elevation: Resting the thumb and keeping it elevated can help reduce swelling and promote healing. Avoid using the thumb for activities that could put stress on the fracture.
2. Surgical Treatment
If the fracture is severe or if the bones are misaligned or displaced, surgery may be necessary. Surgical options include:
- Pinning or Screws: In cases of displaced fractures, the surgeon may insert pins, screws, or plates to stabilize the bones and ensure proper alignment during healing.
- Tendon Repair: If ligaments or tendons are damaged along with the bone, surgery may be required to repair or reattach them.
After surgery, a period of immobilization and physical therapy may be necessary to ensure optimal recovery and restore thumb function.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
The recovery time for a pouce fracturé depends on the severity of the fracture and the treatment method used. For most thumb fractures, it can take anywhere from 6 to 8 weeks for the bone to heal completely. During this time, it’s essential to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully to ensure proper healing.
After the cast or splint is removed, physical therapy may be recommended to restore mobility, strength, and function to the thumb. Rehabilitation exercises often include:
- Range-of-motion exercises to improve flexibility and prevent stiffness.
- Strengthening exercises to rebuild strength in the thumb and hand muscles.
- Functional exercises to improve grip and coordination.
Full recovery can take several months, especially if surgery was required, but most individuals can regain a functional and pain-free thumb with proper care and rehabilitation.
Preventing Future Injuries
To avoid a pouce fracturé in the future, consider the following preventive measures:
- Wear protective gear: If you play sports, especially contact sports, always wear the appropriate protective gear to minimize the risk of hand and thumb injuries.
- Improve bone health: Eating a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, and engaging in weight-bearing exercises, can help strengthen bones and reduce the risk of fractures.
- Use proper techniques: When lifting heavy objects or engaging in activities that require the use of your hands, always use proper techniques to avoid unnecessary stress on your thumb and hand.
Conclusion
A pouce fracturé can be a painful and disruptive injury, but with proper treatment and care, most people can recover fully and return to normal activities. Whether caused by trauma, sports injury, or repetitive stress, it’s important to recognize the symptoms early and seek medical attention to ensure the best possible outcome. By following recommended treatment protocols and engaging in rehabilitation, you can regain full functionality of your thumb and avoid future complications. Remember, the thumb is essential to hand function, and taking care of it is key to maintaining your overall hand health.













Leave a Reply