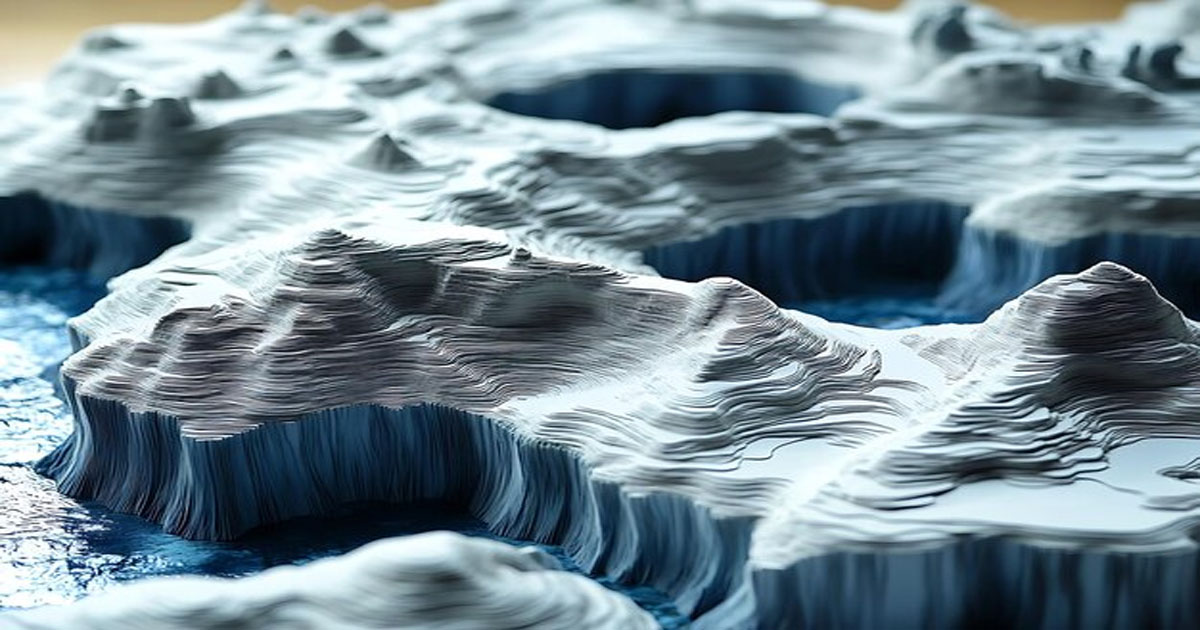
Drifting sheets of ice, often seen in polar and subpolar regions, are a fascinating natural phenomenon. They play a crucial role in our climate system and can impact global weather patterns. This article explores the science behind drifting ice sheets, their effects on the environment, and their significance in climate studies.
What are Drifting Ice Sheets?
Definition and Characteristics
Drifting ice sheets are large, floating masses of ice that move across the ocean’s surface. Unlike icebergs, which are chunks of glaciers that break off into the sea, ice sheets are extensive layers of ice that cover landmasses and extend into the ocean.
Formation and Composition
Ice sheets form from the accumulation of snow over millennia, which compresses into solid ice. They are composed of freshwater and can be thousands of feet thick. As the ice flows from the land into the sea, it creates large floating platforms of ice known as ice shelves.
Types of Ice Sheets
Continental Ice Sheets
Continental ice sheets cover large land areas and are found in Antarctica and Greenland. They are massive in scale and can influence global sea levels when they melt.
Sea Ice Sheets
Sea ice sheets form directly on the ocean’s surface. They are thinner than continental ice sheets and fluctuate seasonally. The Arctic sea ice is a prime example of this type of ice.
The Dynamics of Drifting Ice Sheets
Movement Mechanisms
Ice sheets drift due to various mechanisms, including wind, ocean currents, and the melting of their underside. This movement can be slow, taking years or even decades to travel significant distances.
Impact of Climate Change
Climate change accelerates the melting of ice sheets, leading to a rise in sea levels. The warming temperatures also affect the ice sheet’s structural integrity and its drifting patterns.
Environmental Impact
Rising Sea Levels
As ice sheets melt, they contribute to rising sea levels, which can lead to coastal erosion and flooding. This is a significant concern for low-lying areas and island nations.
Changes in Ocean Circulation
The melting of ice sheets can alter ocean currents and temperatures. This can impact marine life and disrupt weather patterns, leading to unpredictable climate changes.
Ecosystem Effects
Drifting ice sheets can affect local ecosystems by changing habitat conditions. For example, the loss of sea ice impacts polar bears and seals that depend on it for hunting and breeding.
Monitoring and Research
Satellite Observations
Scientists use satellites to monitor the size, movement, and thickness of ice sheets. This data helps in understanding the effects of climate change and predicting future trends.
Field Studies
Field studies involve on-site research to measure ice sheet dynamics and collect samples. These studies provide valuable insights into the ice’s composition and behavior.
Modeling and Predictions
Climate models incorporate data from satellite observations and field studies to predict how drifting ice sheets will behave in the future. These models are crucial for forecasting potential impacts on sea levels and weather patterns.
Historical Context
Past Ice Ages
During the last Ice Age, ice sheets covered much of North America and Europe. Studying these historical ice sheets helps scientists understand past climate changes and their effects on the environment.
Recent Trends
In recent decades, satellite data has shown significant melting of ice sheets, particularly in Greenland and Antarctica. This trend is closely linked to global warming and is a key focus of climate research.
Future Outlook
Projected Ice Loss
Scientists project continued ice loss due to rising global temperatures. This loss is expected to contribute to further sea level rise and changes in ocean circulation.
Mitigation and Adaptation
Efforts to mitigate climate change include reducing greenhouse gas emissions and developing technologies to capture carbon. Adaptation strategies focus on preparing for and managing the impacts of ice loss, such as strengthening coastal defenses.
Conclusion
Drifting sheets of ice are more than just a captivating natural phenomenon; they are a critical component of our planet’s climate system. Understanding their dynamics helps us grasp the broader implications of climate change and prepare for its effects. As we continue to monitor and study these ice sheets, we gain valuable insights into our changing world and the steps we need to take to protect it.












Leave a Reply